Oracle Data Guard ensures high availability, data protection, and disaster recovery for enterprise data. Data Guard provides a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases to enable production Oracle databases to survive disasters and data corruptions. Data Guard maintains these standby databases as copies of the production database. Then, if the production database becomes unavailable because of a planned or an unplanned outage, Data Guard can switch any standby database to the production role, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage. Data Guard can be used with traditional backup, restoration, and cluster techniques to provide a high level of data protection and data availability.
You can manage primary and standby databases using the SQL command-line interfaces or the Data Guard broker interfaces, including a command-line interface (DGMGRL) and a graphical user interface that is integrated in Oracle Enterprise Manager.
The primary database can be either a single-instance Oracle database or an Oracle Real Application Clusters database.
Data Guard Overview
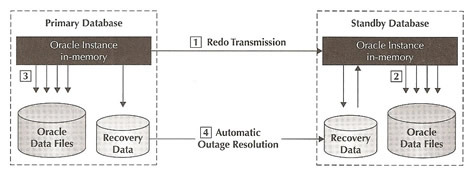
Data Guard is basically a ship redo and then apply redo, as you know redo is the information needed to recover a database transaction. A production database referred to as a primary database transmits redo to one or more independent replicas referred to as standby databases. Standby databases are in a continuous state of recovery, validating and applying redo to maintain synchronization with the primary database. A standby database will also automatically resynchronize if it becomes temporary disconnected to the primary due to power outages, network problems, etc.
The diagram below shows the overview of Data Guard, firstly the redo transport services transmits redo data from the primary to the standby as it is generated, secondly services apply the redo data and update the standby database files, thirdly independently of Data Guard the database writer process updates the primary database files and lastly Data Guard will automatically resynchronize the standby database following power or network outages using redo data that has been archived at the primary.
For more information see:
1.1 Data Guard Configurations
A Data Guard configuration consists of one production database and one or more standby databases. The databases in a Data Guard configuration are connected by Oracle Net and may be dispersed geographically. There are no restrictions on where the databases are located, provided they can communicate with each other. For example, you can have a standby database on the same system as the production database, along with two standby databases on other systems at remote locations.You can manage primary and standby databases using the SQL command-line interfaces or the Data Guard broker interfaces, including a command-line interface (DGMGRL) and a graphical user interface that is integrated in Oracle Enterprise Manager.
1.1.1 Primary Database
A Data Guard configuration contains one production database, also referred to as the primary database, that functions in the primary role. This is the database that is accessed by most of your applications.The primary database can be either a single-instance Oracle database or an Oracle Real Application Clusters database.
Data Guard Overview
Data Guard is basically a ship redo and then apply redo, as you know redo is the information needed to recover a database transaction. A production database referred to as a primary database transmits redo to one or more independent replicas referred to as standby databases. Standby databases are in a continuous state of recovery, validating and applying redo to maintain synchronization with the primary database. A standby database will also automatically resynchronize if it becomes temporary disconnected to the primary due to power outages, network problems, etc.
The diagram below shows the overview of Data Guard, firstly the redo transport services transmits redo data from the primary to the standby as it is generated, secondly services apply the redo data and update the standby database files, thirdly independently of Data Guard the database writer process updates the primary database files and lastly Data Guard will automatically resynchronize the standby database following power or network outages using redo data that has been archived at the primary.

For more information see:
- Oracle9i Data Guard Concepts and Administration
- Data Guard Setup in Oracle Database 11g Release 2
- Data Guard (11gR2) Setup using Oracle Grid Control
 Introduction to Oracle Data Guard
Introduction to Oracle Data Guard Getting Started with Data Guard
Getting Started with Data Guard Creating a Physical Standby Database
Creating a Physical Standby Database Creating a Logical Standby Database
Creating a Logical Standby Database

Post a Comment